You’ve seen them before: that little “How can I help you today?” bubble that pops up in the corner of a website if you’re on the page for long, allowing you to interact with a computer application acting as a customer service rep to get the help you need. Chatbots are becoming more and more popular, especially during this era of remote work. A study by Juniper Research forecasts that chatbots will be responsible for cost savings of over $8 billion per year by 2022, an exponential increase from $20 million in 2017.
Chatbots will be responsible for cost savings of over $8 billion per year by 2022, an exponential increase from $20 million in 2017.
The insurance industry is catching on to this time-saving technology as well, using chatbots for everything from handling policy questions to producing quotes or helping with claims. A 2019 LexisNexis study found that more than 80% of the top US insurers leverage chatbot functionality. But giant corporations aren’t the only ones who can benefit from this application of AI. Widely available chatbot platforms and marketing automation systems have made it easier and more affordable than ever for independent agents to plug a chatbot into their website.
Feeling a little intimidated by the idea of using a chatbot at your agency? This article explains what chatbots are and how they can help your agency, and provides resources for choosing a provider and implementing chatbots at your agency.
This article at a glance:
What are chatbots?
Simply put, a chatbot is a program or application designed to conduct online chat conversations with humans. It receives input by text, speech-to-text, or option selection and provides responses from a predetermined set of options. This is different than live chat, which allows users to chat with a live representative in the same fashion. While chatbots are designed to simulate human conversation, there is not actually a human on the other end of the conversation.
Chatbots are considered a form of artificial intelligence (AI) because they “learn” by becoming more accurate as they acquire more data. There are two main types of chatbot: rule-based and contextual.
Rule-based chatbots |
Contextual chatbots |
|
Simple functionality |
Complex functionality |
|
Simple logic |
Complex logic |
|
Simple implementation |
Complex implementation |
Rule-based chatbots
Rule-based (also called scripted) chatbots are the simplest form of chatbot, functioning as a basic decision tree with if/then statements (if the person says/selects x, then respond with y). The most basic chatbots in this category rely entirely upon menus or buttons, rather than allowing the user to type their request. The user selects an option, and the bot answers with a predefined action or response depending on the selection. This functions somewhat like a phone IVR, where you select a number to signal what you want to do and are provided with further options until you’re directed to the correct information or person.
More sophisticated rule-based chatbots allow free text or speech input and rely instead on keywords to understand a user’s intent. If the person uses a keyword (such as “office hours”), the chatbot provides a predefined response assigned to that keyword or combination of keywords (such as “our office hours are 8am to 5pm, Monday through Friday”).
A rule-based chatbot can help your agency handle the most basic and common requests you receive, while allowing those with more complex requests to schedule a time to meet with a live agent.
Since they’re fairly basic, rule-based chatbots are usually more affordable, quicker, and easier for a business to implement than more complex options. The business simply decides on the logic to use and provides the needed menu options or keywords, as well as the corresponding responses.
However, rule-based chatbots are also limited in their usefulness. If a user doesn’t see the menu option they need, or use a keyword the bot recognizes, the chatbot won’t be able to help them—or it may misinterpret a request because it can only identify keywords, rather than understand the entire conversation. Still, a rule-based chatbot can help your agency handle some of the most basic and common requests you receive, while allowing those with more complex requests to schedule a time to meet with a live agent.
Contextual chatbots
Contextual (or intelligent) chatbots are far more sophisticated than their rule-based counterparts. These bots use natural language processing (NLP) to accurately understand the speech or text of the user. They’re called contextual because they can understand the actual context of a conversation and the intent behind it rather than just scanning text for keywords, similar to how virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa function. For example, if you ask “What time is it in London?” it could respond with the correct time, and if you followed that by asking, “What about Paris?” it could infer that you were still asking about the time and respond correctly, even though time wasn’t included in the second request.
Contextual chatbots can understand and respond with more nuance and fulfill much more complicated requests than rule-based ones. They can provide far more personalized responses and can “learn” from every interaction to help the next one be more relevant. Because of this, they are more expensive and time-consuming to set up, usually requiring custom programming to tailor them to your agency and specific workflows. However, they can also provide exponentially greater value to a business than rule-based chatbots.
Contextual chatbots can understand more complex requests and provide far more personalized responses than rule-based chatbots, and can “learn” from every interaction to help the next one be more relevant.
Why use a chatbot?
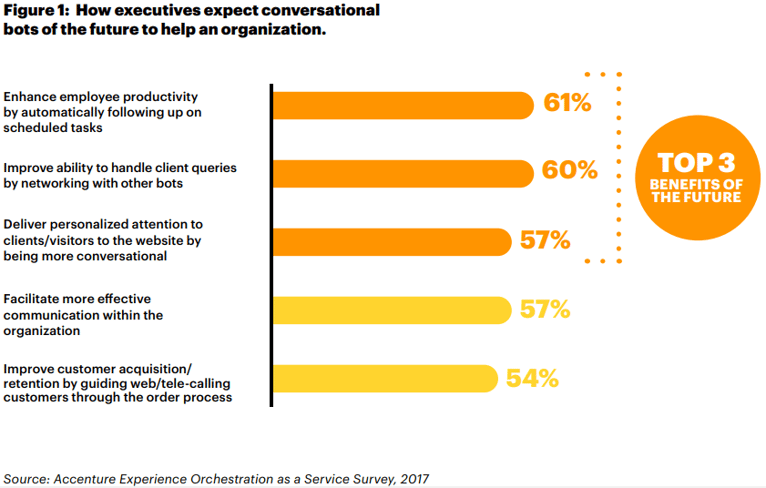
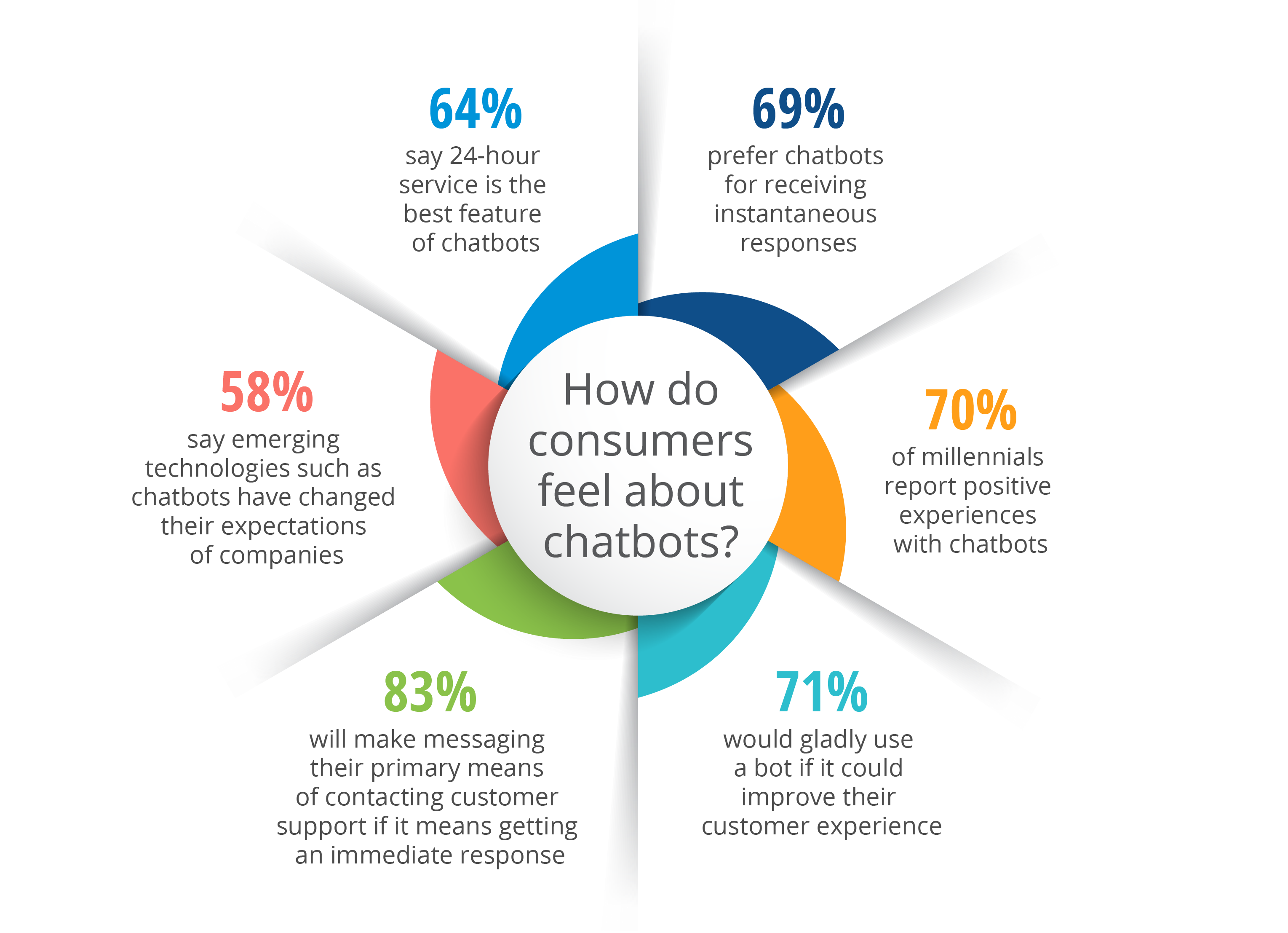
It’s not difficult to see how chatbots can save businesses time and money. They can cut operational costs by up to 30%, and users love having instant, 24/7 access to the answers they need. See the graph below for findings from an Accenture survey on how chatbots can help an organization.
Applications in insurance
How does this translate to your insurance agency? Chatbots can perform countless functions, like answering common questions, directing customers to the resources they’re looking for on your website, booking appointments, or even recommending products or coverage. More complex chatbots can even complete actions on the customer’s account, such as taking payments, collecting forms, providing quotes, guiding customers through the claims process, or even making minor changes to policies. The chart below illustrates some of the most impactful applications of chatbots in the insurance industry, according to a study by Cognizant.
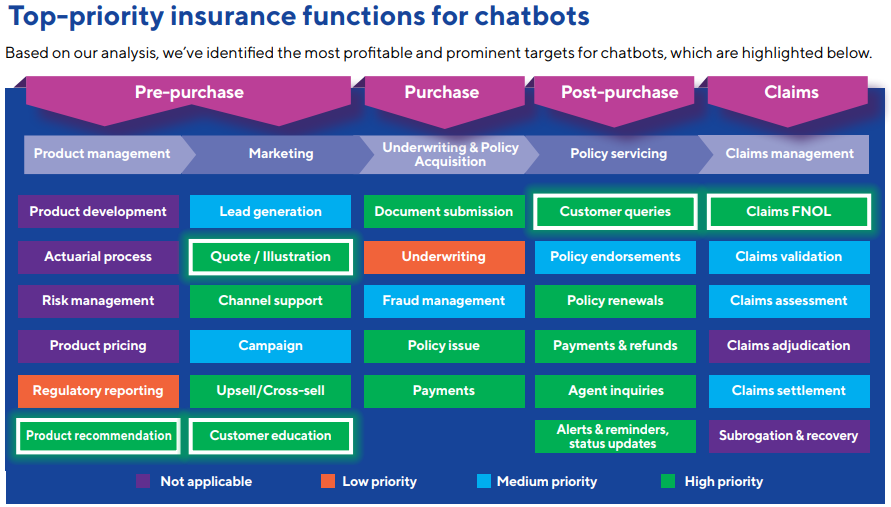 Source: Cognizant
Source: Cognizant
Benefits of chatbots
While there are nearly limitless uses for chatbots, they all provide the same major benefits to the agency:
- 24/7 availability (provide help outside office hours)
- Instant responses (create higher satisfaction and conversion)
- Scalability (assist many customers simultaneously)
- E&O coverage (automatic documentation, fewer human errors)
- Analytics and insights on customer needs, responses, etc.
- Time and personnel savings (free staff for more complex issues)
It’s important to note that chatbots aren’t meant to replace agency staff. Their purpose is simply to handle the more routine tasks so that staff can have more time to deal with complex issues, provide better service to clients, and make more sales.
Finding the right platform
If you’re looking to implement a chatbot platform at your agency, you might want to start by considering those made specifically for the insurance industry, which may already have common insurance workflows built in such as booking appointments, quoting, claims, etc. Here are some of the other top features and functionality to look for when you’re considering chatbot providers.
Integration
Integrates with your CRM, management system, payment provider, e-signature solution, and other technology to perform needed workflows.
Agent handover
Transfers user to live agent when requests are beyond its knowledge.
Transfers user to correct person based on request, region, account owner, etc.
Addresses users by name or gives personalized recommendations based on demographics, search terms, etc.
Pulls information about users from across the web to provide personalized suggestions.
Provides insights on user inquiries and behaviors.
Allows for testing of multiple options to see what customers prefer.
Allows interface to be branded with your agency’s logo, colors, etc.
Has advanced measures in place to protect information entered by customers.
Agency implementation
Once you’ve chosen a chatbot platform, how do you go about implementing it at your agency?
While a chatbot will bring significant time savings to your agency, it requires some time and effort at the outset to get it set up and working smoothly with your agency’s workflows. We’ve outlined the steps we recommend taking when incorporating the use of a chatbot at your agency.
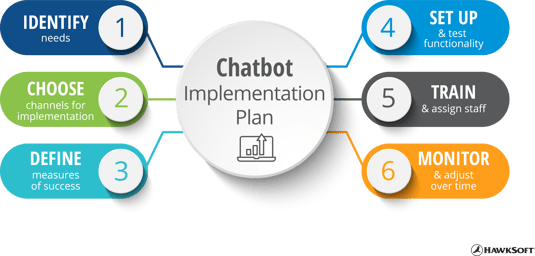
1. Identify needs
2. Choose channels for implementation
While it may sound like a given, you’ll need to decide where you want users to interact with the chatbot. For an independent agency, the place that makes the most sense will likely be your agency’s website, where customers are likely to go when they have a question or need. However, chatbots are often able to interface with social platforms like Facebook Messenger or WhatsApp, so you’ll need to decide the channels where your chatbot will be available.
3. Define measures of success
Come up with a few key performance indicators (KPIs) that you can track to understand the success and ROI for your chatbot. These could be things like the number of requests handled, impact on call volume or hold time, change in customer satisfaction scores, etc. If you don’t see an improvement in these areas within a reasonable amount of time after implementing the chatbot, take another look at your strategy to make sure you’re making the best use of the technology.
4. Set up and test functionality
A chatbot can only be as helpful as it’s been programmed to be. You’ll need to input the menu options or keyword triggers for it to use, as well as the correct answers and resources for each question or selection. Depending on the complexity of the chatbot, there may be custom programming needed to integrate the chatbot with your agency’s specific workflows.
Once you have the chatbot set up to your liking, it’s critically important to test it thoroughly before making it available to customers. This will give you a chance to discover any gaps in functionality and correct errors before customers use it.
5. Train and assign staff
Like we said earlier, chatbots don’t replace humans. Chatbots run most efficiently when they’re being monitored by a live person. You’ll need to assign one or more people to oversee the chatbot—depending on your chatbot’s functionality, it may elevate requests to a person at the agency when they are more complex than it can handle. Make sure your staff understands how the platform works and knows how to make adjustments, handle transferred requests, and perform other needed tasks.
6. Monitor and adjust over time
The first few weeks of live customers using your chatbot will be crucial, as it gathers data and “learns” from its interactions. Monitor its usage closely during this time to identify any errors, missing functionality, or ways customers interact with the chatbot that you might not have expected. You might come across a question you haven’t programmed an answer for, or a specific workflow that needs to be tweaked because customers are getting stuck or giving up. Make adjustments as needed to increase the efficiency of your chatbot.
The period of most adjustment will be within the first few months of implementation, but it’s important to continue to regularly monitor the chatbot on an ongoing basis and make adjustments when processes change or new ones are added. Chatbots interface directly with your customers, so it’s important to make sure they aren’t providing outdated or incorrect information.
For more resources on implementing chatbots at your agency, we recommend looking at ACT’s Chatbot Guide and chatbot page, which includes examples of bots you can test, as well as ITL’s recommendations on integrating chatbots.
Get started with chatbots
Implementing a newer technology like chatbots at your agency might feel intimidating, but with a good background understanding of how they work and a solid plan for implementing them, chatbots can become efficient, valuable, and time-saving members of your agency’s team.
Learn about more uses for Artificial Intelligence in insurance
|